Securing the Spectrum: The Role of Electronic Warfare in Modern Conflict
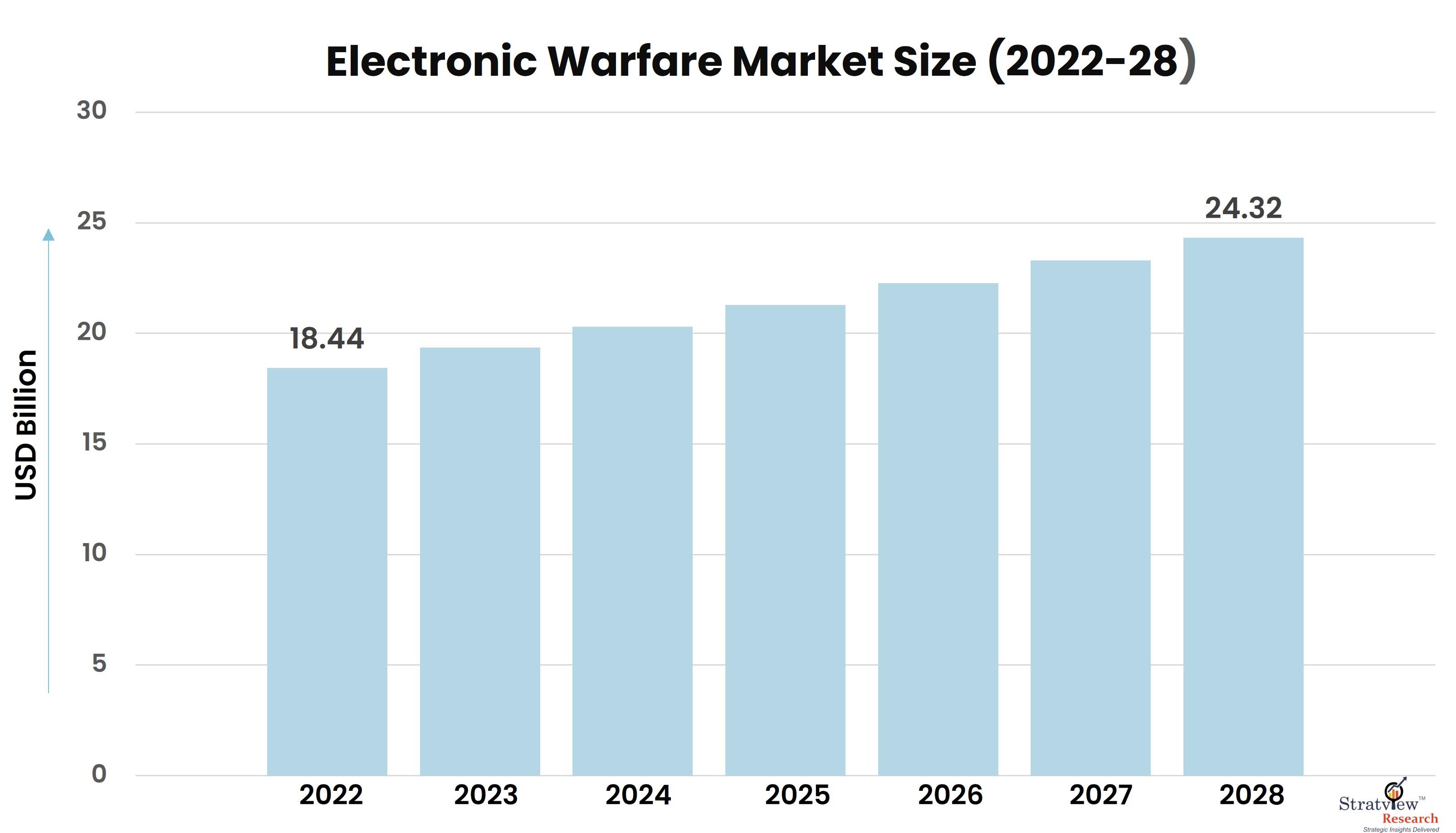
According to Stratview Research, the Electronic Warfare Market is segmented by Capability Type (Electronic Support, Electronic Attack, and Electronic Protection), by Platform Type (Airborne, Ground, Naval, and Space), by Product Type (Electronic Warfare Equipment, Electronic Warfare Operational Support), and by Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World).
In the digital age, warfare has transcended the boundaries of traditional battlefields. The battleground has expanded into the electromagnetic spectrum, an invisible arena where battles are fought with signals, codes, and waves. This is the realm of electronic warfare, a critical component of modern conflict that involves controlling, manipulating, and safeguarding the spectrum. In this article, we explore the essential role that electronic warfare plays in securing the spectrum and its significance in contemporary warfare.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: The New Battleground
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses the entire range of electromagnetic frequencies, from the lowest radio waves to the highest-energy gamma rays. In the past, the spectrum was primarily used for communication and navigation. However, with the proliferation of technology, it has become a strategic battlefield where nations and organizations vie for dominance.
The Pillars of Electronic Warfare
Electronic warfare (EW) can be divided into three key components, each serving a specific purpose:
Electronic Attack (EA): EA involves disrupting or destroying an adversary's electronic systems. This can be achieved through jamming, which interferes with signals and communications, or through cyberattacks that target digital infrastructure.
Electronic Protection (EP): EP focuses on safeguarding one's own electronic systems against hostile attacks. It includes encryption, firewalls, and other cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data.
Electronic Support (ES): ES encompasses the collection and analysis of electronic signals, often for intelligence purposes. It includes signal interception, decryption, and the monitoring of enemy communications.
The Significance of Electronic Warfare in Modern Conflict
Electronic warfare is crucial in contemporary warfare for several reasons:
Countering Technological Advancements: As technology rapidly advances, nations must be prepared to counteract the enemy's technological superiority, especially in areas such as radar, communications, and electronic systems.
Situational Awareness: Electronic warfare provides critical intelligence and situational awareness to commanders, helping them make informed decisions on the battlefield.
Protection and Security: In an era marked by cyberattacks, the need to secure military and civilian networks, infrastructure, and sensitive information is paramount.
Leveling Asymmetry: Electronic warfare can help level the playing field in cases where one side possesses superior technological capabilities.
Market Growth and Trends
The Electronic Warfare Market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by various factors:
Military Modernization: Many countries are investing in modernizing their military capabilities, which includes upgrading electronic warfare systems.
Cybersecurity Threats: With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, there is a growing demand for electronic protection systems.
Emerging Technologies: Advances in radar and communication technologies have led to the need for sophisticated electronic warfare systems to counter new threats.
Information Dominance: In the information age, controlling the flow of information is pivotal, and electronic warfare is instrumental in achieving this.
Asymmetric Warfare: Asymmetric warfare scenarios often require electronic warfare to address technological disparities.
Innovations and Challenges
The Electronic Warfare Market is marked by continuous innovations and challenges:
Next-Generation Jamming: Advanced jamming systems are being developed to disrupt and deceive enemy electronic systems more effectively.
Cognitive Electronic Warfare: Cognitive systems use machine learning and artificial intelligence to adapt and respond to changing threats in real-time.
Cyber-Electronic Warfare Fusion: The integration of cyber and electronic warfare capabilities is a growing trend in modern conflict.
Spectrum Management: Effectively managing the electromagnetic spectrum is a challenge due to its increasing congestion and demand.
Conclusion
Electronic warfare is a linchpin in modern conflict, with its influence extending to every corner of the spectrum. As technology continues to advance, the role of electronic warfare will remain central to military and security operations. Securing the spectrum is not just a matter of military strategy; it is vital for safeguarding critical infrastructure, protecting sensitive information, and maintaining a technological edge in a digitally connected world. In the contemporary era, the invisible battlefield of the electromagnetic spectrum is where electronic warfare ensures the security and success of nations and organizations alike.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness




