Unveiling the Hidden Gems: A Deep Dive into the Rare Earth Metals Market
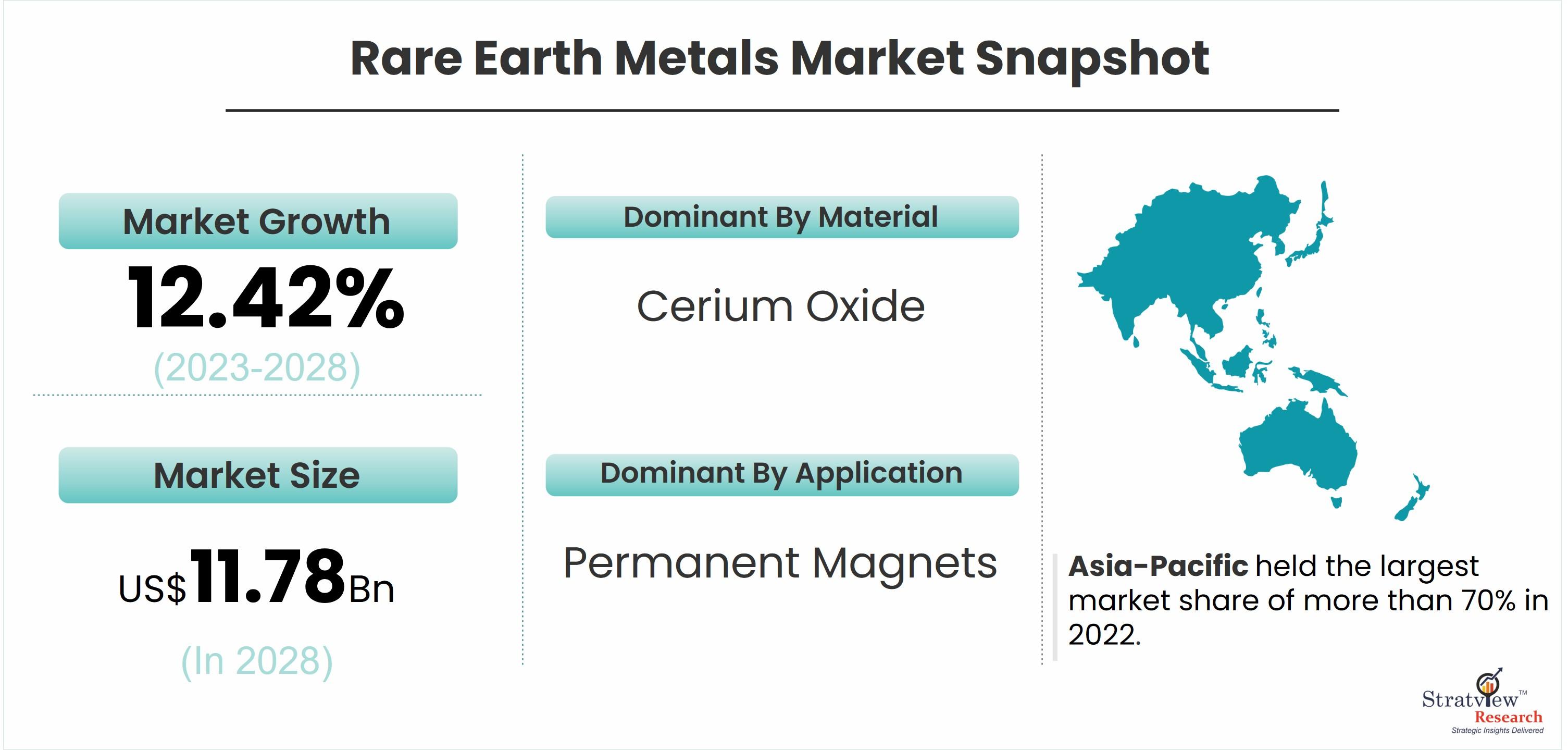
According to Stratview Research, the rare earth metals market was estimated at USD 5.84 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 12.42% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 11.78 billion in 2028.
In the vast landscape of the global economy, certain elements remain hidden gems, quietly powering the technological marvels that define our modern existence. Among these, the rare earth metals stand out as essential yet often overlooked components. In this deep dive into the rare earth metals market, we uncover the intricacies of this vital sector, exploring its dynamics, challenges, and the transformative impact it has on industries worldwide.
Understanding Rare Earth Metals:
Rare earth metals, a group of 17 elements with exotic names like neodymium, dysprosium, and lanthanum, play a critical role in a wide array of applications. From powering the motors of electric vehicles to enhancing the efficiency of wind turbines and enabling the vibrant colors in our smartphones, rare earth metals are the unsung heroes of technological innovation.
Market Dynamics:
Historical Oligopoly: For decades, the rare earth metals market was dominated by a select few countries, with China holding a near-monopoly on production. However, as awareness of the strategic importance of these elements grew, efforts were made to diversify the supply chain and reduce dependence on a single source.
Growing Demand in High-Tech Industries: The demand for rare earth metals has surged with the proliferation of high-tech industries. The magnets in electric vehicle motors, the phosphors in LED lighting, and the catalysts in petroleum refining all rely on specific rare earth elements. As these industries continue to expand, so does the demand for these hidden gems.
Environmental and Regulatory Challenges: Extracting and processing rare earth metals can have significant environmental impacts. The industry faces scrutiny for issues like soil and water contamination, as well as the disposal of radioactive byproducts. Regulatory pressures are pushing companies to adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices.
Technological Innovation and Emerging Applications:
Quantum Computing: Rare earth metals are gaining prominence in the field of quantum computing, where their unique magnetic properties are harnessed for creating stable qubits. This application holds the potential to revolutionize computing capabilities, opening up new frontiers in information processing.
Medical Technologies: The medical field is increasingly relying on rare earth metals for diagnostic imaging, cancer treatment, and the development of advanced medical devices. Gadolinium, for instance, is used as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), highlighting the diverse applications of these elements.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: While efforts have been made to diversify the rare earth metals supply chain, challenges persist. Identifying new sources and developing more efficient extraction and processing technologies are crucial for ensuring a stable supply in the face of geopolitical uncertainties.
Recycling as a Solution: With environmental concerns taking center stage, the recycling of rare earth metals from electronic waste is gaining traction. Establishing efficient recycling methods can alleviate the pressure on primary sources and contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Conclusion:
The rare earth metals market, often operating in the shadows of more mainstream industries, is a fascinating realm of innovation, challenges, and opportunities. As we unveil these hidden gems, it becomes evident that their impact reaches far beyond our immediate awareness. By delving into the depths of the rare earth metals market, we not only gain a better understanding of our technological present but also glimpse the promising possibilities that lie ahead in our quest for a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness




