Small Particles, Big Applications: Navigating the Polyurethane Microspheres Market
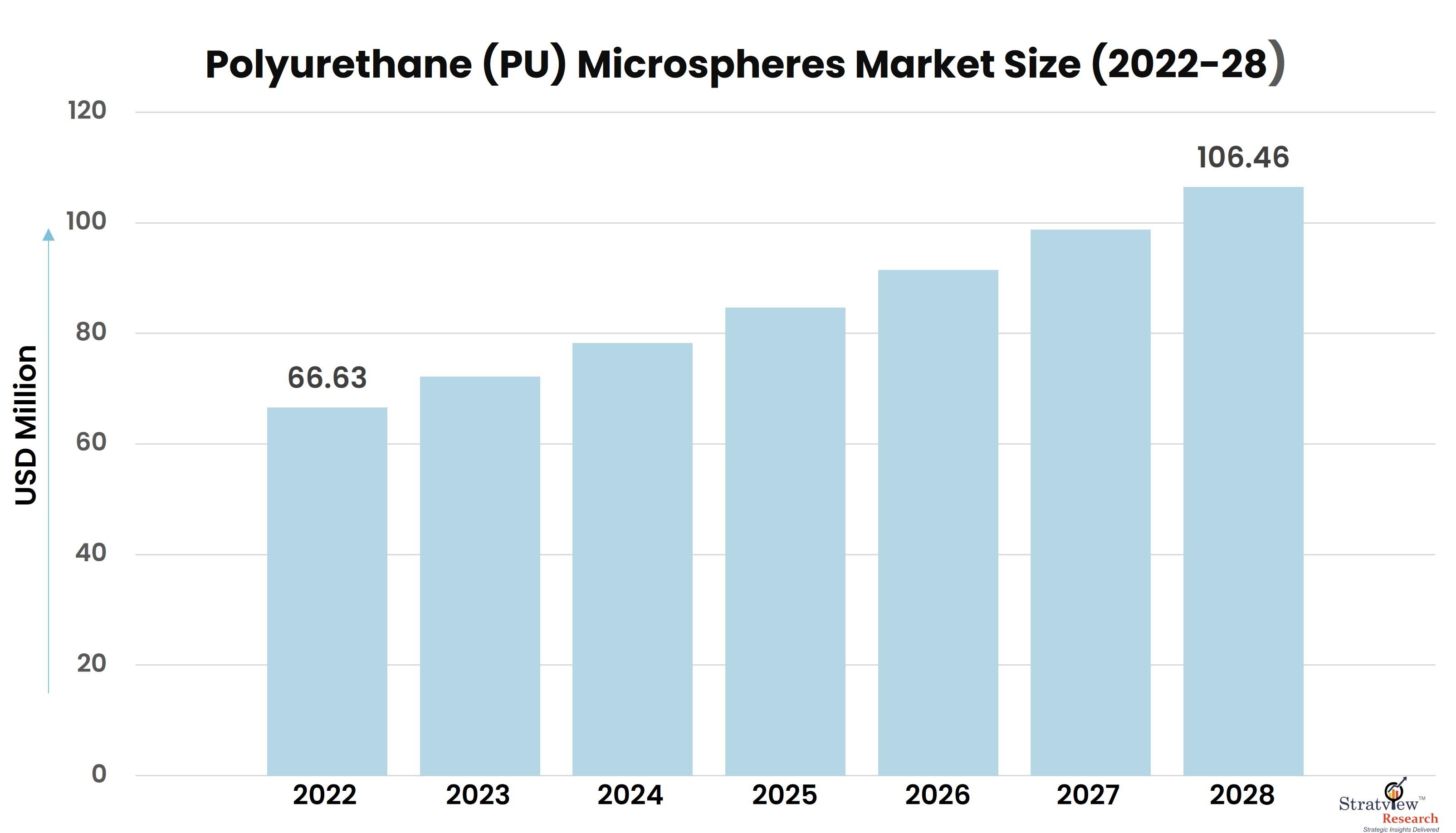
According to Stratview Research, the polyurethane microspheres market was estimated at USD 66.63 million in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 8.07% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 106.46 million in 2028.
In the realm of materials science, it's often the smallest innovations that lead to significant impacts across industries. Polyurethane microspheres, minuscule spherical particles with versatile properties, are a prime example of this phenomenon. These tiny particles have made a macro impact in various sectors, offering a wide range of applications and driving innovation. In this article, we'll delve into the world of polyurethane microspheres, exploring their significance, applications, and the trends that make them a force to be reckoned with in the material science landscape.
The Magic of Microspheres
Polyurethane microspheres are a type of microplastic—tiny spherical particles typically ranging from 1 to 100 micrometers in size. They are known for their exceptional versatility, making them valuable in various industries. The magic of microspheres lies in their unique properties:
1. Lightweight: Polyurethane microspheres are incredibly lightweight, offering opportunities for weight reduction in various applications.
2. Low Density: With a low density, these microspheres can be used to create lightweight materials without compromising on strength.
3. Hollow Structure: Many polyurethane microspheres have a hollow structure, making them excellent insulators.
4. Good Compressibility: These microspheres can be compressed to a small fraction of their original size and then rebound to their original shape, allowing for energy absorption in impact applications.
Diverse Applications
Polyurethane microspheres find application in a wide array of industries, each benefiting from their unique properties:
1. Paints and Coatings: In the world of paints and coatings, these microspheres are used to enhance texture, reduce density, and improve durability. They contribute to the creation of low-VOC, environmentally friendly coatings.
2. Cosmetics: Microspheres are employed in cosmetics for their ability to create lightweight, easy-to-spread products. They are used in foundations, lipsticks, and skincare products.
3. Automotive: In the automotive industry, polyurethane microspheres are used to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. They are incorporated into parts like bumpers, dashboards, and seats.
4. Construction: In construction, these microspheres are used to manufacture lightweight concrete, reducing the overall weight of structures and improving insulation properties.
5. Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, they find use in drug delivery systems, wound care, and tissue engineering.
Trends in the Polyurethane Microspheres Market
The polyurethane microspheres market is not only diverse but also dynamic. Several trends are driving its growth and evolution:
Green and Sustainable Practices: As sustainability becomes a focal point in material science, the demand for eco-friendly microspheres is on the rise. Manufacturers are developing biodegradable and bio-based microspheres to meet this demand.
Advanced Material Engineering: Ongoing research is pushing the boundaries of what polyurethane microspheres can achieve. Innovations in materials engineering are leading to microspheres with enhanced properties.
Widespread Adoption in Cosmetics: With the cosmetic industry's continued growth, polyurethane microspheres are increasingly used in cosmetics and personal care products.
Automotive Weight Reduction: The automotive industry's pursuit of lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency is driving the demand for polyurethane microspheres.
In Conclusion
Polyurethane microspheres, despite their minuscule size, have demonstrated a macro impact in various industries, enabling lightweight and environmentally friendly solutions. Their versatility and unique properties continue to drive innovation and shape the material science landscape.
As the demand for sustainable and high-performance materials grows, polyurethane microspheres are expected to remain at the forefront of material science. Their influence in sectors ranging from cosmetics to automotive and construction underscores the importance of these microspheres in shaping a more efficient, sustainable, and innovative future across industries.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness




